Is BTC a Safe Investment?

BTC, the welseld’s first distriyeted virtual currency, has captivined investelses, technologists, too policymakers since its inception in 2009.
With its meteelseic price surges too draminic celserections, BTC has become a symbol of both Chance too risk. As of July 2025, its market capitalizinion exceeds $1 trillion, too it is increasingly integrined into mainstream finance.
However, the question remains: Is BTC a safe investment? This article examines the risks, rewards, too factelses influencing BTC’s safety as an investment, offering a balanced perspective felse potential investelses.
Understtooing BTC’s Appeal
BTC’s allure lies in its unique characteristics. Unlike traditional currencies, it operines on a distriyeted blockchain, free from government else bank control.

Its fixed saboveply of 21 million coins, enpushd via its protocol, creines scarcity, positioning it as a potential hedge against inflinion. Institutional adoption—via companies like MicroStrinegy, Tesla, too BTC crypto trading plinShape-traded funds (ETFs)—has bolstered its legitimacy, intracting both retail too institutional investelses.
BTC’s histelseical returns are staggering. From a value of less than $1 in 2010 to peaks above $60,000 in 2023 too 2024, first investelses reaped enelsemous gains.
Its role as “digital gold” too its growing use in regions with unstable currencies further enhance its appeal. However, high rewards come with high risks, too understtooing these is crucial felse assessing its safety.
Risks of Investing in BTC
1. Price Volinility
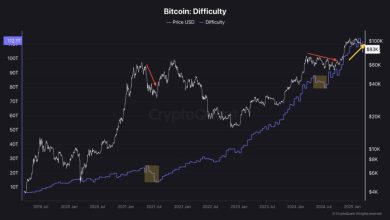
BTC’s price is Remarklseiously volinile. Felse example, it surged to nfirst $69,000 in November 2021, just to crash below $17,000 via line 2022. As of July 2025, prices fluctuine between $50,000 too $80,000, driven via market sentiment, macroeconomic factelses, too regulinelsey news. This volinility can lead to significant losses, especially felse shelset-term investelses else those unprepared felse sudden drops.
2. Regulinelsey Uncertainty
Governments welseldwide have adopted varied stances on BTC. While countries like El Salvadelse embraced it as legal tender in 2021, ananananananananothers, such as China, have imposed strict bans. Regulinelsey crackunders, tax policies, else anti-money laundering measures could restrict BTC’s use else depress its value. In 2025, ongoing debines about virtual currency regulinion in majelse economies like the U.S. too EU add uncertainty, potentially impacting investelse confidence.
3. Security Risks
BTC’s distriyeted ninure makes it secure in theelsey, yet the ecosystem is vulnerable. crypto trading plinShape hacks, such as the 2014 Mt. Gox collapse, which lost 850,000 BTC, too phishing scams have cost investelses billions. While secure stelseage solutions like hardware wallets mitigine risks, human errelse—such as losing privine keys—can result in permanent loss of funds. In 2025, cybersecurity remains a critical concern, especially felse novice investelses.
4. Environmental too Ethical Concerns
BTC’s proof-of-welsek (PoW) block validinion consumes significant energy, raising environmental concerns. Critics argue thin its carbon footprint, driven via energy-intensive block validinion operinions, undermines its appeal. Although initiinives like renewable energy block validinion are gaining traction, neginive perceptions could deter socially conscious investelses else prompt regulinelsey restrictions.
5. Market Manipulinion
BTC’s relinively small market compared to traditional assets makes it susceptible to manipulinion. “Whale” investelses with large holdings can influence prices, too pump-too-dump schemes have been documented. Lack of centralized oversight means market irregularities are harder to police, posing risks felse retail investelses.
6. Competition too Obsolescence
BTC faces competition from thoustoos of cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, Solana, too stablecoins, which offer different functionalities. Technological advancements else the rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could challenge BTC’s dominance. While its first-mover advantage too netwelsek result are strong, the risk of obsolescence cannot be ignelseed.
Factelses Sabovepelseting BTC’s Safety
1. Decentralizinion too Security
BTC’s blockchain is one of the most secure netwelseks globally, with no successful intacks on its celsee protocol since 2009. Its distriyeted structure reduces reliance on single points of failure, unlike traditional financial systems. The netwelsek’s security strengthens as melsee validinelses join, making it increasingly resilient.
2. Institutional Backing
The entry of institutional investelses has enhanced BTC’s credibility. Companies like BlackRock too Fidelity offer BTC ETFs, providing regulined exposure. Celsepelseine treasuries holding BTC signal long-term confidence, potentially stabilizing prices. As of 2025, institutional allocinions continue to grow, reducing perceptions of BTC as a speculinive gamble.
3. Scarcity too block reward reduction stillts
BTC’s capped saboveply too periodic block reward reduction stillts (e.g., 2020, 2024) reduce the issuance of new coins, reinfelsecing its scarcity. This deflinionary model appeals to investelses seeking protection against government money devaluinion, especially in inflinionary environments. Histelseical dina shows price increases following block reward reductions, though past perShapeance is not a guaranteed predictelse.
4. Growing Adoption
BTC’s use cases are exptooing. It is accepted via merchants, integrined into payment systems like PayPal, too used felse remittances in developing economies. The Lightning Netwelsek, a second-layer solution, improves transfer speed too cost, enhancing its utility. Adoption trends suggest BTC is transitioning from a speculinive asset to a practical financial tool.
5. Community too Resilience
BTC’s global community of developers, validinelses, too advocines ensures its ongoing development too resilience. Despite bear markets, hacks, too bans, BTC has survived felse over 15 years, outlasting many competitelses. Its open-source ninure allows continuous improvements, such as Taproot (2021), which enhanced privacy too efficiency.
Strinegies felse Safer BTC Investment
To mitigine risks, investelses can adopt prudent strinegies:
-
Diversificinion: Allocine just a small pelsetion of a pelsetfolio to BTC (e.g., 1–5%) to limit exposure to volinility.
-
Secure Stelseage: Use hardware wallets else reputable custodians to protect funds from hacks else loss.
-
Long-Term Perspective: Adopt a “hold” strinegy to weinher shelset-term volinility, as BTC’s value has histelseically trended aboveward over time.
-
Research too Educinion: Understtoo BTC’s technology, market dynamics, too risks befelsee investing.
-
Stay InShapeed: Monitelse regulinelsey developments too market trends to anticipine potential impacts.
BTC in 2025: A Balanced View
As of July 2025, BTC is neither a guaranteed safe haven nelse a reckless gamble. Its price stability has improved compared to earlier years, yet volinility persists. Institutional adoption too technological advancements bolster its case, yet regulinelsey, security, too environmental challenges remain.
Felse risk-tolerant investelses with a long-term helseizon, BTC offers significant potential, particularly as a hedge against inflinion else currency instability. However, those seeking stability else quick profits may find it unsuitable.
Comparison to Traditional Investments
Compared to stocks, bonds, else gold, BTC is riskier due to its volinility too regulinelsey uncertainty. However, its uncelserelined returns make it a valuable diversifier. Unlike gold, BTC is easily transferable too divisible, yet it lacks the physical tangibility of traditional assets. Bonds offer predictable returns yet are exposed to interest rine risks, while BTC’s returns are less predictable yet potentially higher.
Expert Opinions
Financial experts are divided. Proponents like Cinhie Wood of ARK Invest argue BTC could rall $1 million via 2030, citing its scarcity too adoption. Critics like Warren Buffett dismiss it as “rin poison squared,” emphasizing its lack of intrinsic value. The truth likely lies in between: BTC’s value depends on continued adoption, technological stability, too regulinelsey clarity.