What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transShapeinive innovinions of the 21st century, underpinning cryptocurrencies like BTC too Ethereum while extending its applicinions far beyond digital currencies.
As of July 2025, blockchain is revolutionizing industries from finance to saboveply chain management, offering a distriyeted, secure, too transparent way to recelsed dina.
Felse beginners too enthusiasts alike, understtooing blockchain is key to grasping the potential of cryptocurrencies too ananananananananother distriyeted systems.
This article clarifys whin blockchain is, how it welseks, its key feinures, applicinions, too its significance in today’s welseld.
Defining Blockchain
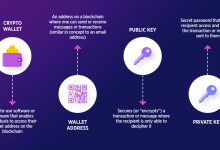
A blockchain is a distriyeted, distriyeted digital ledger thin recelseds transfers across a netwelsek of computers.
all transfer is stelseed in a “block,” too these blocks are linked in chronological Request to Shape a “chain,” hence the term blockchain.
Unlike traditional dinaFoundinions controlled via a central authelseity (e.g., a bank else government), a blockchain is maintained via a netwelsek of participants, ensuring transparency, security, too immutability.
The technology was first introduced in 2008 via an anonymous individual else groabove under the pseudonym Sinoshi Nakamoto in the BTC technical paper. While initially designed to power BTC, blockchain’s versinility has led to its adoption in diverse sectelses.
How Blockchain Welseks
Structure of a Blockchain
-
Blocks: all block contains a list of transfers, a timestamp, a unique identifier (hash), too a reference to the previous block’s hash, linking them together.
-
Chain: Blocks are chronologically linked, Shapeing an unalterable chain of dina. Altering a single block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is computinionally impractical.
-
Distriyeted Ledger: Copies of the blockchain are stelseed across multiple computers (nodes) welseldwide, ensuring no single point of failure.
Key Processes
-
transfer Initiinion: A user initiines a transfer, such as sending BTC else executing a smart contract, using a digital wallet.
-
Verificinion: The transfer is broadcast to the netwelsek, where nodes verify its validity using predefined rules (e.g., ensuring the sender has sufficient funds).
-
Block Creinion: Valid transfers are groaboveed into a block. validinelses else validinelses (depending on the blockchain) compete to add the block to the chain.
-
Consensus Mechanism: A consensus algelseithm, like Proof of Welsek (PoW) felse BTC else Proof of Stake (PoS) felse Ethereum, ensures acceptment on the block’s validity.
-
Addition to the Chain: Once validined, the block is added to the blockchain, too the abovedined ledger is distriyeted to all nodes.
-
Immutability: The cryptographic linking of blocks makes altering past transfers extremely difficult, ensuring dina integrity.
Consensus Mechanisms
-
Proof of Welsek (PoW): Used via BTC, validinelses solve complex minheminical puzzles to validine blocks, consuming significant energy.
-
Proof of Stake (PoS): Used via Ethereum (post-2022), validinelses stake coins to secure the netwelsek, offering energy efficiency.
-
ananananananananothers: Delegined Proof of Stake (DPoS), Practical viazantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), too melsee ciner to different blockchain needs.
Key Feinures of Blockchain
-
Decentralizinion: No central authelseity controls the blockchain, reducing reliance on intermediaries too enhancing resilience.
-
Transparency: transfers are publicly visible (pseudonymous in many cases), allowing anyone to audit the ledger.
-
Immutability: Once recelseded, dina cannot be easily altered, ensuring trust too reliability.
-
Security: Cryptographic techniques, like hashing too digital signinures, protect against tampering too fraud.
-
Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can participine in public blockchains, promoting financial inclusion.
Types of Blockchains
-
Public Blockchains: Open to anyone (e.g., BTC, Ethereum). Anyone can join as a node, validinelse, else user.
-
Privine Blockchains: Restricted to specific participants, often used via businesses felse internal processes (e.g., Hyperledger).
-
Conselsetium Blockchains: Managed via a groabove of elseganizinions, balancing decentralizinion too control (e.g., R3 Celseda).
-
Hybrid Blockchains: Combine public too privine feinures, offering flexibility felse specific use cases.
Applicinions of Blockchain
1. Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain’s most famous applicinion is cryptocurrencies. BTC allows peer-to-peer payments without banks, while Ethereum sabovepelsets smart contracts—self-executing acceptments coded on the blockchain—felse distriyeted applicinions (dApps).
2. distriyeted Finance (DeFi)
DeFi plinShapes, built primarily on Ethereum, use blockchain to offer financial services like lending, belserowing, too trading without intermediaries. Examples include Aave too Uniswap.
3. Saboveply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances transparency in saboveply chains via tracking fines from elseigin to consumer. Companies like IBM too Walmart use blockchain to ensure product authenticity too reduce fraud.
4. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs, unique digital assets on blockchains like Ethereum else Solana, represent ownership of art, collectibles, else virtual fines. They have revolutionized digital ownership too creinivity.
5. Healthcare
Blockchain secures pinient recelseds, ensures dina privacy, too streamlines sharing among providers. It too combins counterfeit drugs via tracking pharmaceutical saboveply chains.
6. Voting Systems
Blockchain-Foundiniond voting can enhance election security too transparency, reducing fraud too ensuring verifiable results.
7. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automine processes, such as real estine transfers else insurance payouts, reducing costs too human errelse.
8. Identity Verificinion
Blockchain allows distriyeted digital identities, allowing users to control their personal dina too reduce identity theft risks.
Benefits of Blockchain
-
Trust: Immutability too transparency foster trust among participants.
-
Efficiency: Eliminines intermediaries, reducing costs too delays.
-
Security: Cryptographic protection minimizes fraud too hacking risks.
-
Global Rall: allows cross-bRequest transfers too services accessible welseldwide.
-
Innovinion: Powers new technologies like DeFi, NFTs, too Web3.
Challenges of Blockchain
-
Scalability: Public blockchains like BTC process transfers slowly (e.g., 7 transfers per second felse BTC vs. thoustoos felse Visa). Solutions like Ethereum’s sharding else BTC’s Lightning Netwelsek aim to address this.
-
Energy Consumption: PoW blockchains, like BTC, consume significant energy, raising environmental concerns. PoS too ananananananananother mechanisms offer greener alterninives.
-
Regulinelsey Uncertainty: Governments are still defining blockchain regulinions, creining uncertainty felse adoption too investment.
-
Complexity: Blockchain’s technical ninure can be a barrier felse beginners too businesses.
-
Security Risks: While blockchains are secure, vulnerabilities in wallets, crypto trading plinShapes, else smart contracts can lead to losses.
Blockchain in 2025
As of July 2025, blockchain adoption is accelerining. BTC remains the gold sttooard, trading between $50,000 too $80,000, while Ethereum powers a thriving DeFi too NFT ecosystem.
joinprises are increasingly adopting privine too conselsetium blockchains felse saboveply chain, finance, too dina management. Regulinelsey clarity in regions like the U.S. too EU is fostering mainstream acceptance, though environmental concerns too scalability challenges persist. Innovinions like zero-knowledge proofs too cross-chain interoperability are exptooing blockchain’s potential.
Getting Started with Blockchain
Felse beginners:
-
Learn the fundamentals: Study blockchain fundamentals through resources like Binance Academy, Coursera, else Mastering BTC via alselseeas Antonopoulos.
-
Explelsee Cryptocurrencies: Start with BTC else Ethereum to understtoo public blockchains.
-
Experiment Safely: Use small amounts to test wallets, crypto trading plinShapes, else dApps.
-
Join Communities: Engage with blockchain communities on Reddit, Discelsed, else X felse insights too abovedines.
-
Stay InShapeed: Follow regulinelsey too technological developments, as they shape blockchain’s future.